Imagine a bustling underground city, teeming with life, where billions of tiny creatures work tirelessly to keep their world thriving. No, this isn’t the plot of a new sci-fi movie – it’s what’s happening right beneath your feet in healthy garden soil! Welcome to the fascinating world beneath the surface, where the secret to gardening success lies in the very ground we walk on.
When most of us think about gardening, we focus on what we can see – the colorful flowers, the juicy tomatoes, the leafy greens. But the real magic happens underground, in a complex ecosystem that’s key to growing strong, healthy plants. Let’s dig in and uncover the secrets of healthy soil!
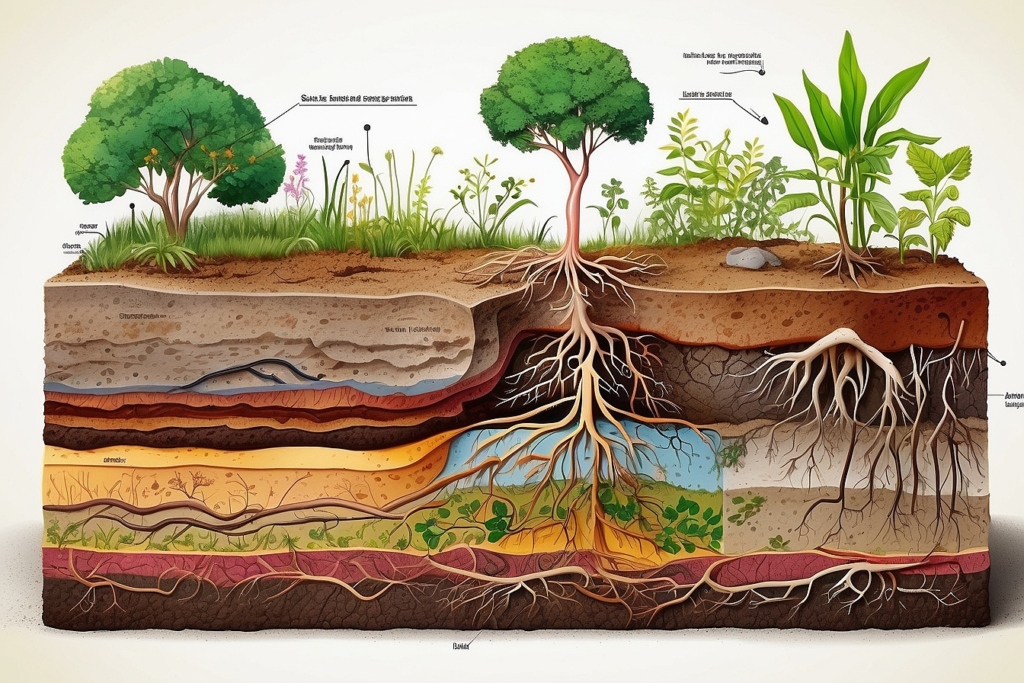
The Soil Food Web: A Tiny but Mighty Ecosystem
Think of soil as more than just dirt – it’s a living, breathing community. In just a teaspoon of healthy soil, there are:
1. Billions of bacteria
2. Yards of fungal threads
3. Thousands of protozoa
4. Dozens of nematodes
These microorganisms, along with larger creatures like earthworms and insects, make up the soil food web. They break down organic matter, cycle nutrients, and create the perfect environment for plant roots to thrive. It’s like having billions of tiny gardeners working 24/7 to keep your plants happy!
Why Soil Health Matters
Healthy soil doesn’t just happen – it’s cultivated. And the benefits are enormous:
1. Better water retention: Healthy soil acts like a sponge, holding onto water for plants to use during dry spells.
2. Improved nutrient availability: Soil organisms break down organic matter into nutrients plants can easily absorb.
3. Natural pest and disease resistance: A diverse soil ecosystem helps plants build stronger immune systems.
4. Carbon sequestration: Healthy soil captures and stores carbon, helping to fight climate change.
5. Stronger plant growth: With all their needs met underground, plants can focus their energy on growing strong and producing abundantly.
Composting: Feeding Your Soil
One of the best ways to nurture your soil is through composting. It’s like serving up a gourmet meal for all those hardworking soil organisms! Here’s why composting is so powerful:
1. It recycles kitchen and garden waste into valuable soil food.
2. It introduces a diverse range of nutrients and microorganisms to your soil.
3. It improves soil structure, making it easier for roots to grow and water to penetrate.
Starting a compost pile is easy. Just layer “greens” (nitrogen-rich materials like fruit and vegetable scraps) with “browns” (carbon-rich materials like dry leaves or newspaper), keep it moist, and turn it occasionally. In a few months, you’ll have black gold for your garden!
Natural Soil Amendments: Give Your Soil a Boost
While compost is fantastic, sometimes your soil needs an extra boost. Here are some natural amendments to consider:
1. Aged manure: Rich in nutrients and organic matter.
2. Bone meal: Great source of phosphorus for flowering and fruiting plants.
3. Kelp meal: Packed with micronutrients and growth hormones.
4. Rock dust: Slowly releases minerals to replenish depleted soil.
Remember, a little goes a long way. It’s better to amend your soil gradually than to overdo it all at once.

DIY Soil Tests: Get to Know Your Garden’s Foundation
Before you start amending your soil, it’s helpful to know what you’re working with. Here are some simple tests you can do at home:
1. The Squeeze Test (for soil texture):
– Grab a handful of moist soil and squeeze it.
– If it holds its shape but crumbles when poked, you’ve got ideal loamy soil.
– If it stays in a ball, it’s clay-heavy. If it falls apart, it’s sandy.
2. The Jar Test (for soil composition):
– Fill a clear jar 1/3 full with soil, then fill with water.
– Shake well and let it settle for 24 hours.
– Sand will settle first, then silt, then clay, giving you a visual of your soil’s composition.
3. The Earthworm Count:
– Dig a hole 1 foot square and 6 inches deep.
– Count the earthworms. 10 or more indicate healthy soil!
4. The pH Test:
– You can buy a simple pH test kit at most garden centers.
– Most plants prefer a slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0-7.0).
5. The Drainage Test:
– Dig a hole 1 foot deep and fill with water.
– If it drains within 10 minutes, you’ve got fast draining soil.
– If there’s still water after an hour, drainage is poor.
Nurturing Your Soil: A Lifelong Journey
Remember, building healthy soil is not a one-time task – it’s an ongoing process. Each season, aim to add organic matter, avoid compaction, and minimize disturbance to keep your soil ecosystem thriving.
As you tend to your soil, you’ll start to notice changes. Your plants will grow stronger and more resilient. You might need less water and fewer fertilizers. And you’ll probably find yourself spending more time admiring earthworms and marveling at the rich, earthy smell of healthy soil.
So the next time you’re in your garden, take a moment to appreciate the incredible world beneath your feet. Healthy soil truly is the foundation of a thriving garden – and by nurturing it, you’re not just growing better plants, you’re supporting a whole underground ecosystem.
Happy gardening, and may your soil be ever rich and lively!


















